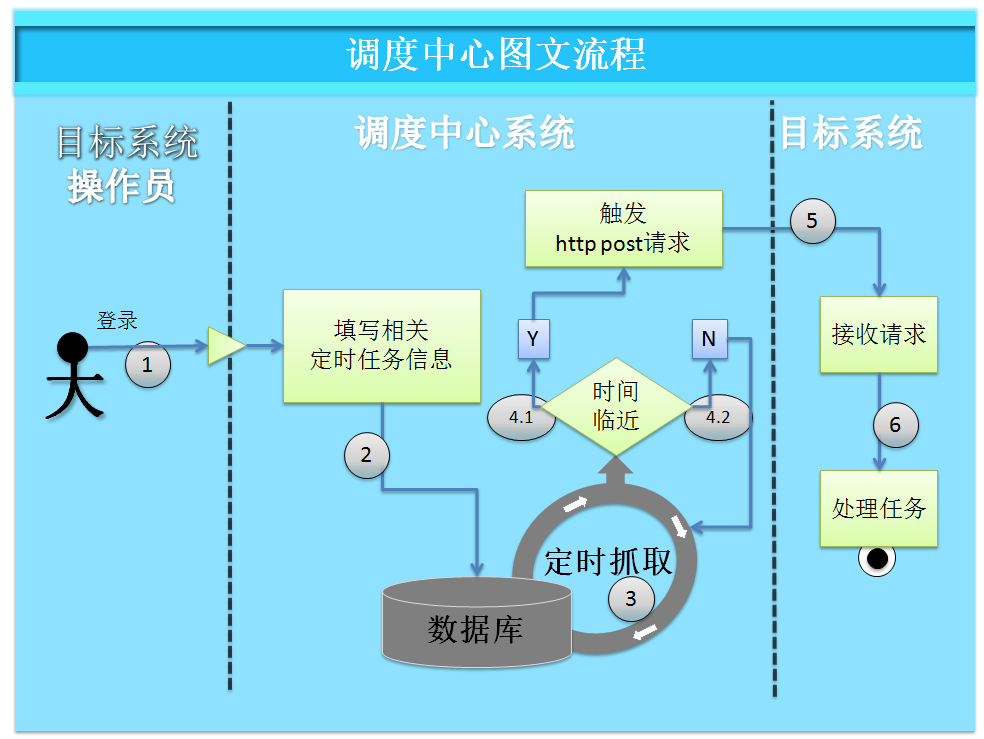
任务调度中心
主要依赖quartz.jar相关类 判断cron表达式 , 在下次即将执行的时间在指定时间内时, 从线程池中取线程进行调度 (优化版)
为什么要有调度中心
因为在集群环境,多server都会在同一时间执行相同定时任务,那么此时定时任务的并发会造成大量数据重复或其它不可预知的业务异常.而调度中心只会按间隔触发一次请求给集群中的负载去分发.不会造成重复触发的情况.
场景
前台工作人员录入定时任务信息入TBL_TASK表后, 调度中心以很短的间隔定时全量抓取库 TBL_TASK表判断表达式时间是否临近10秒以内,如果临近了,就触发请求给目标系统,让目标系统进行真正的业务处理(比如进行百万级别的数据同步),然后只需要返回一个成功失败标志告诉调度中心,最终统一从调度中心去观察任务正常与否.也方便了集中管理任务调度.
只要配置好相关信息,就不用在spring或java 等trigger中去配置定时任务了.
下载资料
定时任务quartz 包 : quartz-2.2.3.zip
项目源码 : http://pan.baidu.com/s/1nu9oK4p
git地址: https://git.oschina.net/KingBoBo/TimeTaskDispatcherCenter.git
相关表:
TBL_TASK表结构如下,您不必建表,此处只是假设有这样的表存在而以.为了方便演示,最终只是模拟取数,并不会真正从数据库中取该表数据
| 主键 | 任务名 | 调度中心调度地址 | 执行间隔表达式 |
| C_ID | C_NAME | C_URL | C_EXPRESSION |
| employeeTask | 调用X系统进行员工信息同步 | http://www.xxx.com/syncEmployees | 0/10 * * * * ? |
| carTask | 调用Y系统进行车辆信息同 | http://www.yyy.com/syncCars | 0 0/1 * * * ? |
相关类:
MyTask.java
普通任务Bean,对应数据表 TBL_TASK


package com.king; /** * 普通任务javaBean,从数据库取到数据到放到该对象中 * @author King * */ public class MyTask { String id; String name; String url; String expression; long delayMillis;// 延迟执行时间 单位毫秒 boolean isApproaching; public MyTask(String id, String name, String url, String expression) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.url = url; this.expression = expression; } public String getExpression() { return expression; } public void setExpression(String expression) { this.expression = expression; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public long getDelayMillis() { return delayMillis; } public void setDelayMillis(long delayMillis) { this.delayMillis = delayMillis; } public boolean isApproaching() { return isApproaching; } public void setApproaching(boolean isApproaching) { this.isApproaching = isApproaching; } @Override public String toString() { return "MyTask [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", url=" + url + "]"; } }
TaskDao.java
模拟对TASK表进行CRUD操作的Dao层
package com.king; /** * 模拟dao层从数据库取数据,及更新数据 * @author King * */ public class TaskDao { /** * 生成2个定时任务,用来模拟定时任务表 * @return */ public MyTask[] querySomeTasks() { // 10秒一次 MyTask employeeTask = new MyTask("employeeTask", "调用X系统的servlet,进行员工信息同步", "http://www.baidu.com", "0/10 * * * * ?"); // 20秒一次 MyTask carTask = new MyTask("carTask", "调用Y系统的servlet,进行车辆信息同步", "http://www.baidu.com", "0 0/1 * * * ?"); MyTask[] tasks = new MyTask[] { employeeTask, carTask }; return tasks; } /** * 更新 * @return */ public String updateSomething() { return ""; } }
MyCallable.java
线程调用类,由public static final ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(30);池调用
package com.king; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; /** * 受线程池管控的线程类 * @author King * */ public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> { //固定30个线程的线程池,如果定时任务的个数超过该值,有一定可能造成任务等待. //但不一定会发生,这要看是否有30多个任务是否都集中在同一时间点上触发 public static final ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(30); private MyTask task; private static String encoding = "UTF-8"; private Map runningMap; private static final SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS"); @Override public String call() throws Exception { String returnData = "success";// 模拟返回信息 System.out.println(); System.out.println("任务开始时间:【" + sdf.format(new Date()) + "】"); try { Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000); System.out.println("【模拟】用java.net.HttpURLConnection发外围传进来的task" + task);// 此处用打印语句模拟真实发送 System.out.println("【模拟】返回报文为: " + returnData); System.out.println("【模拟】信息返回后更新表TaskDao.updateSomething()"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { runningMap.remove(task.getId()); } System.out.println("任务结束时间:【" + sdf.format(new Date()) + "】"); System.out.println(); return returnData; } public MyTask getTask() { return task; } public void setTask(MyTask task) { this.task = task; } public Map getRunningMap() { return runningMap; } public void setRunningMap(Map runningMap) { this.runningMap = runningMap; } }
TimeTaskDispatcherCenter.java
任务调度中心主类,Main()方法模拟了10次调度.
实际主要模拟了,从数据库中取到task表中信息,判断表达式时间是否临近10秒,如果临近了就从池中取线程延迟一定时间后执行该task任务
package com.king; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Date; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import org.quartz.CronExpression; /** * 定时任务调度中心 * @author King * */ public class TimeTaskDispatcherCenter { private static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS"); private static final int APPROACH_SECONDS = 10;// 临近时间 单位秒 // 线程安全的map private static final Map RUNNING_MAP = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap()); public void dispatch() { System.out.println("执行中的任务:" + RUNNING_MAP.keySet().toString()); // 模拟从从数据库取task数据 TaskDao dao = new TaskDao(); MyTask[] tasks = dao.querySomeTasks(); for (MyTask task : tasks) { if (judgeAppropching(task)) {// 如果即将执行的时间临近当前时间10秒内 if (RUNNING_MAP.containsKey(task.getId())) {// 如果运行中的任务已包含当前任务,不执行该任务 continue; } else { RUNNING_MAP.put(task.getId(), task); execute(task);// 从池中取线程,运行该task } } } } /** * 如果字符串代表的cron表达式时间临近,返回true * * @param task * 当expression字符串为空或cron表达式为空,返回false * @return */ private boolean judgeAppropching(MyTask task) { CronExpression cron = null; try { cron = new CronExpression(task.getExpression());// 把字符串转换成cron表达式,用以计算下次执行时间 } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (cron != null) {// 如果expression正确 // 获取下次执行时间点 (long) Date nextValidDate = cron.getNextValidTimeAfter(new Date()); long nextValidTimeMills = nextValidDate.getTime(); // 计算 下次执行时间点和系统当前时间点 时间差 (delaymillis毫秒) long delayMillis = nextValidTimeMills - System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("任务" + task.getId() + "\t\t\t【下次执行时间预计为:】" + sdf.format(nextValidDate) + "距离当前时间还差" + delayMillis / 1000 + "秒左右"); // 如果 0秒<时间差<10秒 ,返回true if (delayMillis > 0 && delayMillis < APPROACH_SECONDS * 1000) { task.setDelayMillis(delayMillis);// 这一句话很重要,设置了延迟执行时间,execute()方法体中需要该延迟时间 return true; } else { return false; } } else { return false; } } /** * 如果字符串代表的cron表达式时间临近,返回true * * @param expression * 当expression字符串为空或cron表达式为空,返回false * @return */ private boolean judgeAppropching(String expression) { CronExpression cron = null; try { cron = new CronExpression(expression);// 把字符串转换成cron表达式,用以计算下次执行时间 } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (cron != null) {// 如果expression正确 // 获取下次执行时间点 (long) Date nextValidDate = cron.getNextValidTimeAfter(new Date()); long nextValidTimeMills = nextValidDate.getTime(); // 计算 下次执行时间点和系统当前时间点 时间差 (delaymillis毫秒) long delayMillis = nextValidTimeMills - System.currentTimeMillis(); // 如果 0秒<时间差<10秒 ,返回true System.out.println("【下次执行时间预计为:】" + sdf.format(nextValidDate) + "距离当前时间还差" + delayMillis / 1000 + "秒左右"); if (delayMillis > 0 && delayMillis < APPROACH_SECONDS * 1000) { return true; } else { return false; } } else { return false; } } private void execute(MyTask task) { MyCallable call = new MyCallable(); call.setTask(task); call.setRunningMap(RUNNING_MAP); // 调度该任务,但延迟一定毫秒 ,judgeAppropching()会把延迟时间设置进去 MyCallable.executor.schedule(call, task.getDelayMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } // 实际主要模拟了,从数据库中取到task表中信息,判断表达式时间是否临近10秒,如果临近了就从池中取线程延迟一定时间后执行该task任务 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { TimeTaskDispatcherCenter center = new TimeTaskDispatcherCenter(); // center.judgeAppropching("0/10 * * * * ?"); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //真实场景用while(true) center.dispatch(); Thread.currentThread().sleep(2000);// 隔2秒去数据库取全表数据进行调度 } } }
打印结果
由于是多线程,小部分打印语句可能会互相穿插
执行中的任务:[] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:40 000距离当前时间还差8秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差28秒左右 执行中的任务:[employeeTask] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:40 000距离当前时间还差6秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差26秒左右 执行中的任务:[employeeTask] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:40 000距离当前时间还差4秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差24秒左右 执行中的任务:[employeeTask] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:40 000距离当前时间还差2秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差22秒左右 执行中的任务:[employeeTask] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:40 000距离当前时间还差0秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差20秒左右 任务开始时间:【2016-09-02 16:33:40 006】 【模拟】用java.net.HttpURLConnection发外围传进来的taskMyTask [id=employeeTask, name=调用X系统的servlet,进行员工信息同步, url=http://www.xxx.com/syncEmployees] 【模拟】返回报文为: success 【模拟】信息返回后更新表TaskDao.updateSomething() 任务结束时间:【2016-09-02 16:33:41 007】 执行中的任务:[] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:50 000距离当前时间还差8秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差18秒左右 执行中的任务:[employeeTask] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:50 000距离当前时间还差6秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差16秒左右 执行中的任务:[employeeTask] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:50 000距离当前时间还差4秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差14秒左右 执行中的任务:[employeeTask] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:50 000距离当前时间还差2秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差12秒左右 执行中的任务:[employeeTask] 任务employeeTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:33:50 000距离当前时间还差0秒左右 任务carTask 【下次执行时间预计为:】2016-09-02 16:34:00 000距离当前时间还差10秒左右 任务开始时间:【2016-09-02 16:33:50 002】 【模拟】用java.net.HttpURLConnection发外围传进来的taskMyTask [id=employeeTask, name=调用X系统的servlet,进行员工信息同步, url=http://www.xxx.com/syncEmployees] 【模拟】返回报文为: success 【模拟】信息返回后更新表TaskDao.updateSomething() 任务结束时间:【2016-09-02 16:33:51 003】
其它
判断cron表达式是否有效
比如checkCronExpression("0/10 * * * * ? 2018")
private boolean checkCronExpression(String cron){ boolean b=false; try{ CronExpression ce = new CronExpression(cron); Date date = ce.getNextValidTimeAfter(new Date()); if(date != null){ b=true; } }catch (ParseException e) { logger.error(e.getMessage(),e); } return b; }